Premium Quality 3D CAD Files for Your Engineering Projects
3D CAD Files Collections Info for 3D CAD Engineers Gate valves vs Ball Valves
Designing process systems: Gate valves vs ball valves
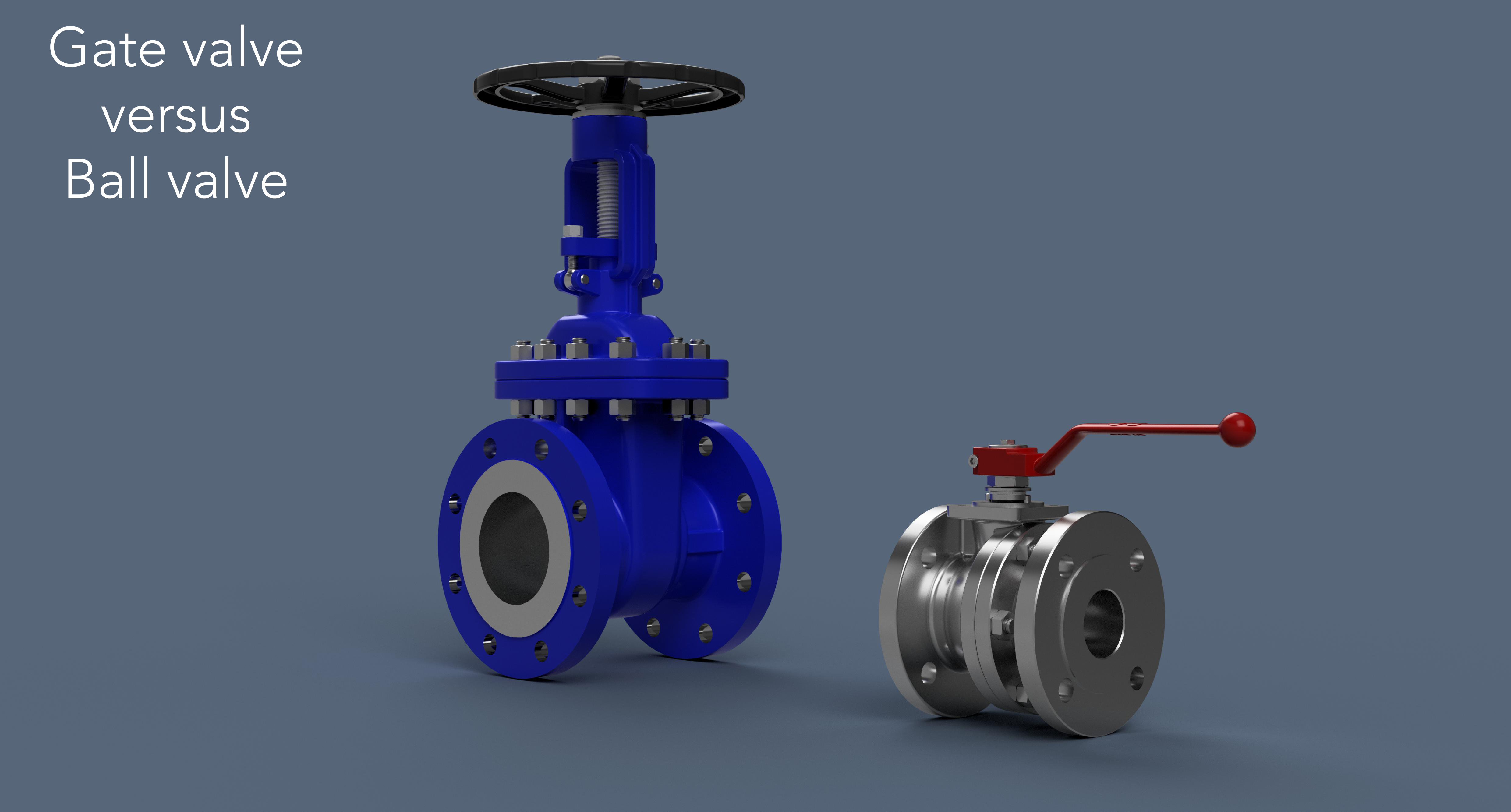

10 Differences between gate valves and ball valves:
1. Design
Gate valves consist of a valve that moves linearly up and down within the valve body. This valve moves vertically to control the flow of the medium.
Ball valves use a spherical ball with a through hole. When the lever or handwheel is rotated, the ball within the valve rotates to open or close the flow passage.
2. Type of closure
Gate valves use linear motion to control the flow. By moving the valve up or down, the flow opening is enlarged or reduced.
Ball valves use a rotating motion to open or close. When the lever or handwheel is turned, the ball inside the valve rotates to open or close the flow passage.
3. Flow rate
Gate valves may cause higher pressure drops compared to ball valves, especially when fully closed, due to the linear motion of the valve. This can lead to higher energy costs and reduced efficiency in high-pressure systems.
Ball valves are known for their lower pressure drops, even when fully closed. The spherical ball minimizes resistance to flow, resulting in more efficient flow of the medium and lower operational costs.
4. On/off control
Gate valves are primarily used as on/off valves, meaning they mainly serve to completely shut off or allow full flow of the medium. This on/off functionality is ideal for applications where rapid and complete shut-off is required, such as in water and gas pipelines.
Ball valves can be used for both on/off control and for regulating the flow of the medium. By partially rotating the lever or handwheel, the user can adjust the flow rate to the specific requirements of the process. This makes ball valves more versatile in their applications.
5. Maintenance
Gate valves can generally be more complex in design and construction, which may result in more maintenance requirements. The linear motion of the valve can cause wear on the seals and the seat, necessitating periodic maintenance and part replacement.
Ball valves generally have a simpler design and construction, resulting in fewer maintenance requirements. The rotating motion of the ball minimizes wear on the seals and the seat, making ball valves typically more maintenance-friendly and having a longer lifespan.
6. Applications
Gate valves are often used in applications where complete shut-off of the flow is required, such as in industrial processes, water and gas pipelines, and sewage and irrigation systems. Their robust design makes them suitable for both low and high-pressure applications.
Ball valves are more versatile in their applications and can be used in a wide range of industries and applications. They are suitable for both on/off closure and for regulating the flow of fluids and gases, making them popular in the chemical industry, oil and gas industry, HVAC systems, and household applications.
7. Pressure range
Gate valves are generally suitable for higher pressure applications due to their robust construction and linear motion. They can be used in high-pressure systems up to several thousands of psi (pounds per square inch).
Ball valves have a wide pressure range and are suitable for both low and medium-pressure applications. They can be used in systems with pressures ranging from a few psi to several hundred psi, depending on the material and construction of the valve.
8. Price
Gate valves tend to be more cost-effective compared to ball valves, especially in larger sizes and for higher pressure applications. However, this cost difference may vary depending on factors such as material, manufacturer, and specific application requirements.
Ball valves are generally more expensive than gate valves, particularly in smaller sizes and for low-pressure applications. The higher cost is often attributed to their precision engineering, versatile functionality, and wider range of applications.
9. Suitable diameters
Gate valves are suitable for a wide range of pipe diameters, ranging from small diameters of around 1/2 inch to very large diameters of several feet or more. They are commonly used in both residential and industrial piping systems.
Ball valves are also available in various sizes, typically ranging from 1/4 inch to 12 inches or more in diameter. They are used in a diverse range of applications, from household plumbing to large industrial processes.
10. Installation
Gate valves require a vertical orientation for optimal performance due to the linear motion of the gate. They are less tolerant of horizontal installation compared to ball valves.
Ball valves are versatile and can be installed in various orientations, including vertical, horizontal, or even upside down. Their spherical design allows for smooth operation regardless of orientation.
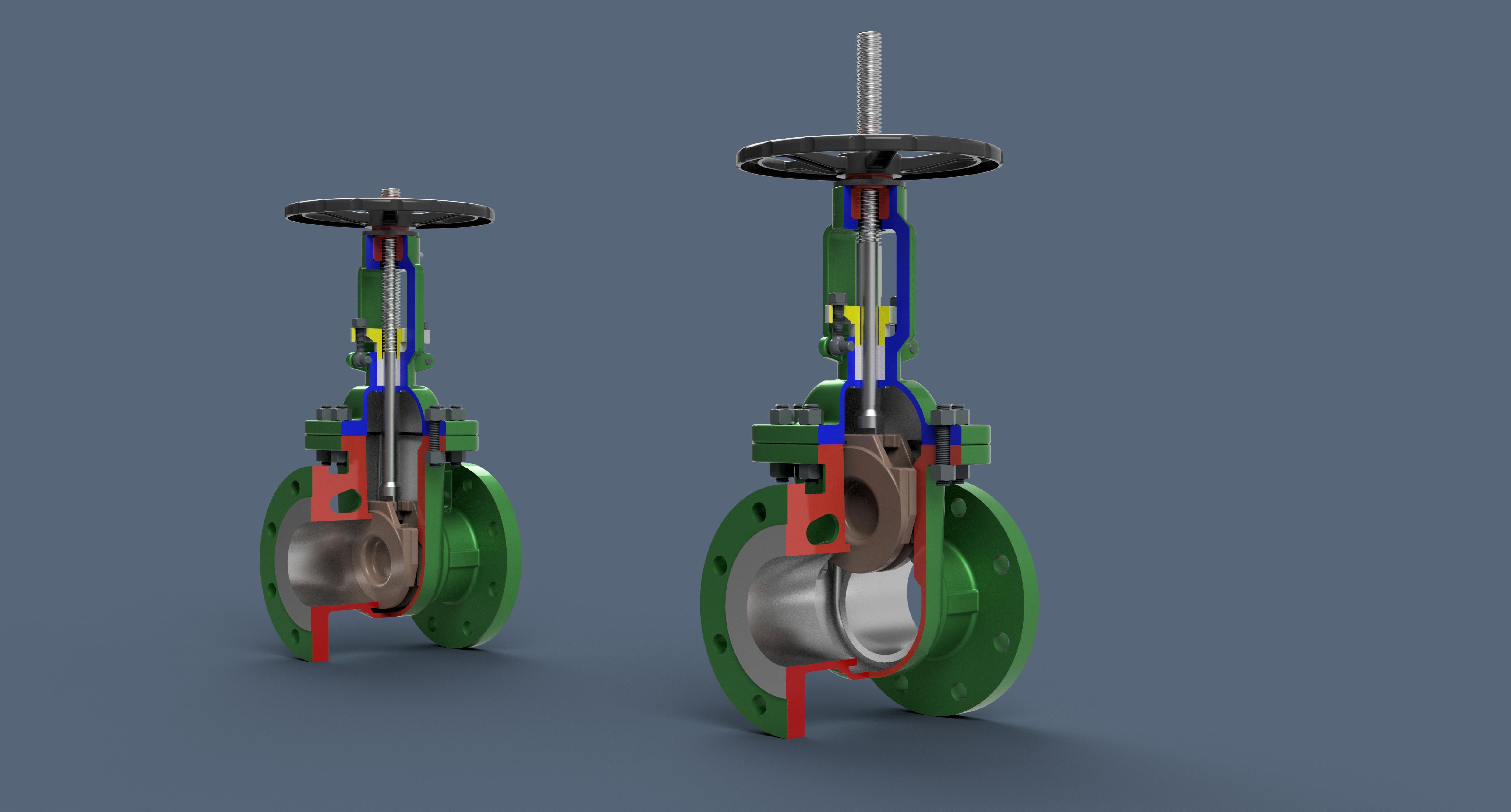
Gate valves: the main fuctions
Isolation: A gate valve can be used to isolate a section of a piping system by fully opening or closing the valve. This allows for maintenance, replacement of parts, or repairs to be carried out without affecting the rest of the system.
Flow Control: Although gate valves are primarily used as on/off valves, they can also be used to regulate the flow of liquids or gases. By partially opening the valve, the user can adjust the flow rate according to the requirements of the process.
Minimal Pressure Drop: Gate valves generally provide minimal pressure drop across the valve when fully open, making them ideal for applications where minimal resistance to flow is required. This makes them suitable for use in systems with high flow velocities and where pressure loss needs to be kept to a minimum.
Ball valves: the main fuctions
Flow control: A ball valve can be used to control the flow of liquids or gases in a piping system. By turning the lever or handwheel of the ball valve, the user can open or close the valve, initiating, stopping, or regulating the flow.
Shut-off: A ball valve can be used as a shut-off valve to completely stop the flow of liquids or gases. When the lever or handwheel of the ball valve is in the closed position, the ball inside the valve is rotated, completely shutting off the passage and stopping the flow.
Safety: Ball valves can be used for safety purposes, such as quickly shutting off a pipeline in case of an emergency, such as a leak or an undesired increase in pressure. The rapid response time of a ball valve makes it a reliable tool for quickly interrupting the flow in critical situations, which can help prevent damage or injury.
Conclusion:
If you are dealing with a pipe with a smaller diameter, the ball valve is usually your best option. It has 2 major advantages:
1. cheaper
2. faster closure of a flow.
A gate valve opens and closes slower, but much more controlled, but that can also be an advantage.
In pipes with a large diameter, a ball valve can simply no longer be operated with a lever and the gate valve is then often the right choice when it comes to these two options.
Check out our 3D CAD Libraries
BSP Threaded Industrial Fittings and Valves - 500 STEP FilesDownload this complete 3D CAD library (6 zip files) and get access to 500 premium quality BSP threaded fittings! (in STEP file format). |
DIN-EN Industrial Weld Fittings and Flanges - 1400 STEP FilesDownload this complete 3D CAD library (2 zip files) and get access to 1400 premium quality industrial DIN-EN fittings (in STEP file format). |
Three Phase IEC Induction Motors - 72 STEP FilesDownload this complete 3D CAD library (2 zip files) and get access to 72 premium quality electric motors! (in STEP file format). |
Industrial Metal Valves DIN-EN Flanges - 1600 STEP FilesDownload this complete 3D CAD library (45 zip files) and get access to 1600 premium quality industrial valves (in STEP file format). |



